Laboratory diamonds have the broadest spectral range of any known material, from the ultraviolet to the far infrared and microwave. Combined with their mechanical and thermal properties, diamonds are ideal for laser optics and laser applications.
The diamonds are available in every color imaginable, with countless shades, tones and levels of saturation. Color comes from inclusions at the atomic level trapped in the crystal lattice of the stone.

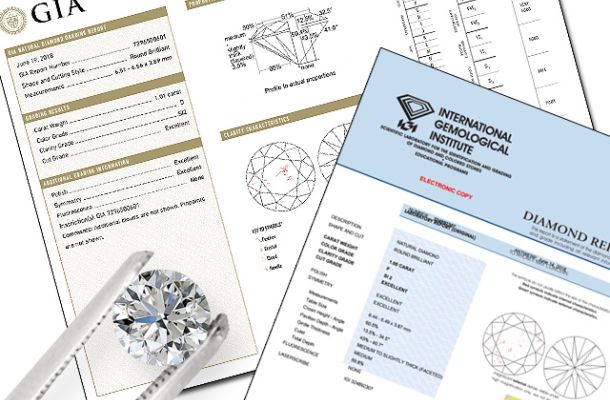
Lab-grown diamonds undergo grading using identical standards as natural diamonds, with the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) providing Laboratory-Grown Diamond Reports that adhere to the standard GIA color, clarity, and cut grading scales. These reports facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of lab-grown diamonds, ensuring consistency and transparency in the grading process.
Color has 3 main components:
- Shade. The aspect that gives the color its name, such as yellow or blue.
- Tone. The lightness or darkness of the color.
- Saturation. The intensity and strength of the color.
Hence, the classification.
Shop Quality Over Quantity
Finally, it’s important to consider the quality of the diamond, regardless of its color. The 4Cs – carat weight, cut, color, and clarity – all play a role in determining a diamond’s value and beauty. A well-cut, clear lab grown diamond with a vibrant hue will truly sparkle.

Laboratory-created diamonds are grown in three stunning colors – yellow, blue and colorless. These colors are permanent, never changing, never fading with time or exposure to temperature.
Let’s take a closer look:
White Diamonds (Colorless). Most people can recognize the luster and sparkle of a diamond. These man-made diamonds are the most desirable of all lab-grown diamonds. Growing colorless diamonds is difficult and time-consuming. To create a colorless diamond, the impurities nitrogen (yellow hue) and boron (blue hue) must be prevented from entering the crystal lattice during growth. Excluding the impurities and limiting the growth of these elements greatly slows the growth rate of the crystal. Colorless diamonds are the most popular, but they are less available, even as one-carat diamonds.
Blue Diamonds. Blue diamonds range in color from a brilliant sky blue to a dark rich blue, up to 1.25 carats. The blue color comes from the presence of boron. These diamonds are harder to grow than yellow diamonds.
Yellow Diamonds. Yellow diamonds are available in colors ranging from a charming bright lemon color to a subtle pale yellow color and reach up to 2 carats. The yellow color comes from impurities of nitrogen. Orange is also acceptable and gives the diamond a fiery vibrancy.
However, not only colorless, blue and yellow stones can be grown in the laboratory, but also diamonds of any other color: pink, green, red and other colors can also be produced.